Statistics
-
Cool Fire Technology. (2004). Charles Dow, the History of the Dow Jones. Averages. Retrieved from http://www.cftech.com/BrainBank/FINANCE/DowJonesAvgsHist.html.
 When Dow came to Wall Street, the investment market of choice was bonds. Investors liked securities that were backed by real machinery, factories and other hard assets. They felt reassured by the predictability of income that bonds offered, as well as the specific dates of maturity when their principle would be returned. The stock market, by contrast, dealt in "shares of ownership'' which had no specific claim on anything a company owned.
When Dow came to Wall Street, the investment market of choice was bonds. Investors liked securities that were backed by real machinery, factories and other hard assets. They felt reassured by the predictability of income that bonds offered, as well as the specific dates of maturity when their principle would be returned. The stock market, by contrast, dealt in "shares of ownership'' which had no specific claim on anything a company owned. -
University of Virginia Library. (2015). Historical census browser. Retrieved from http://mapserver.lib.virginia.edu/
 Examine state and county topics for individual census years.
Examine state and county topics for individual census years. -
Value Stock Guide. (n.d.). The Great Depression – the stock market crash and beyond. Retrieved from http://valuestockguide.com/the-great-depression-the-stock-market-crash-and-beyond/.
 By the time that Franklin Delano Roosevelt was inaugurated as President in 1933, one fourth of the entire American population was unemployed.
By the time that Franklin Delano Roosevelt was inaugurated as President in 1933, one fourth of the entire American population was unemployed.
The Economic Situation
-
Amadeo, K. (n.d.). Stock market crash of 1929: cause, effect and facts. Retrieved from http://useconomy.about.com/od/glossary/g/Stock-Market-Crash-of-1929.htm
 The stock market crash of 1929 was the most significant crash in U.S. history. Although the crash itself only lasted four days, it led to a catastrophic sell-off.
The stock market crash of 1929 was the most significant crash in U.S. history. Although the crash itself only lasted four days, it led to a catastrophic sell-off. -
Smiley, G. (n.d.) The Great Depression. Retrieved from http://www.econlib.org/library/Enc/GreatDepression.html.
 A worldwide depression struck countries with market economies at the end of the 1920s. Although the Great Depression was relatively mild in some countries, it was severe in others, particularly in the United States, where, at its nadir in 1933, 25 percent of all workers and 37 percent of all nonfarm workers were completely out of work.
A worldwide depression struck countries with market economies at the end of the 1920s. Although the Great Depression was relatively mild in some countries, it was severe in others, particularly in the United States, where, at its nadir in 1933, 25 percent of all workers and 37 percent of all nonfarm workers were completely out of work. -
Economic History Association. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://eh.net/?s=great+depression
 This website provides resources from scholars in economic history. Search "The Great Depression" and scroll to access articles on this topic.
This website provides resources from scholars in economic history. Search "The Great Depression" and scroll to access articles on this topic.
Timelines
-
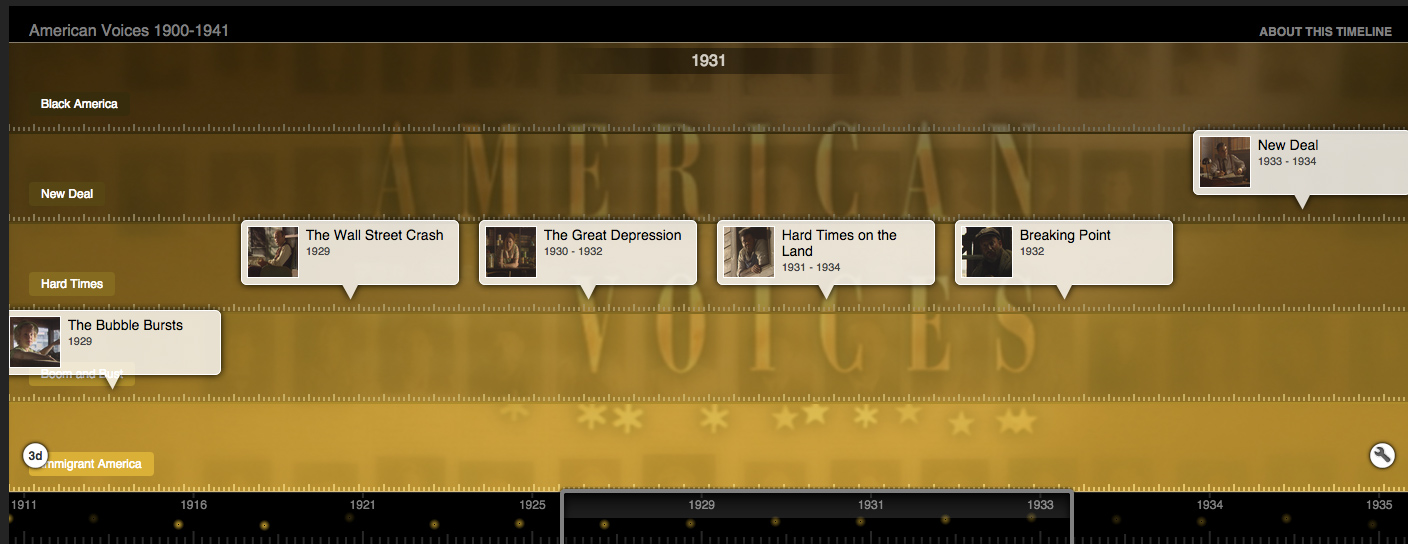
Chater, A. (n.d.). Timeline American voices. Retrieved from http://timelines.tv/mobile/usa1900-4/.
 "American Voices" presents a video history of the USA from 1917 to 1941 - an era of immigration, boom and bust, Depression and New Deal. It reconstructs the extraordinary testimonies of everyday Americans interviewed in the late 1930s by the Federal Writers' Project - testimonies available online in the "Life Memories" Project of the Library of Congress.
"American Voices" presents a video history of the USA from 1917 to 1941 - an era of immigration, boom and bust, Depression and New Deal. It reconstructs the extraordinary testimonies of everyday Americans interviewed in the late 1930s by the Federal Writers' Project - testimonies available online in the "Life Memories" Project of the Library of Congress. -
America’s Great Depression timeline. (2011). Retrieved from http://www.amatecon.com/gd/gdtimeline.html
 America's Great Depression is regarded as having begun in 1929 with the Stock Market crash, and ended in 1941 with America's entry into World War II.
America's Great Depression is regarded as having begun in 1929 with the Stock Market crash, and ended in 1941 with America's entry into World War II. -
Kangas, S. (n.d.). Timelines of The Great Depression. Retrieved from http://www.hyperhistory.com/online_n2/connections_n2/great_depression.html.
 During World War I, federal spending grows three times larger than tax collections. When the government cuts back spending to balance the budget in 1920, a severe recession results. However, the war economy invested heavily in the manufacturing sector, and the next decade will see an explosion of productivity... although only for certain sectors of the economy.
During World War I, federal spending grows three times larger than tax collections. When the government cuts back spending to balance the budget in 1920, a severe recession results. However, the war economy invested heavily in the manufacturing sector, and the next decade will see an explosion of productivity... although only for certain sectors of the economy. -
National Institute of Food and Agriculture. (2014). Growing a nation historical timeline – 1930. Retrieved from http://www.agclassroom.org/gan/timeline/1930.htm
 1932 - Farm prices and income reach "depression" bottom.
1932 - Farm prices and income reach "depression" bottom. -
Iowa Pathways. (2015). Iowa history timeline. Retrieved from http://www.iptv.org/iowapathways/timeline_text.cfm?timeChunkStart=1930&timeChunkEnd=1939
 1930 - Dust Bowl. The Dust Bowl covers the Midwest as topsoil was whipped across the country.
1930 - Dust Bowl. The Dust Bowl covers the Midwest as topsoil was whipped across the country. -
AFL-CIO. (2015). Retrieved from http://www.aflcio.org/About/Our-History/Labor-History-Timeline
 Labor history timeline.
Labor history timeline.