Resource Key

LEVEL 1
brief, basic information laid out in an easy-to-read format. May use informal language. (Includes most news articles)

LEVEL 2
provides additional background information and further reading. Introduces some subject-specific language.

LEVEL 3
lengthy, detailed information. Frequently uses technical/subject-specific language. (Includes most analytical articles)
How do antibiotics work?
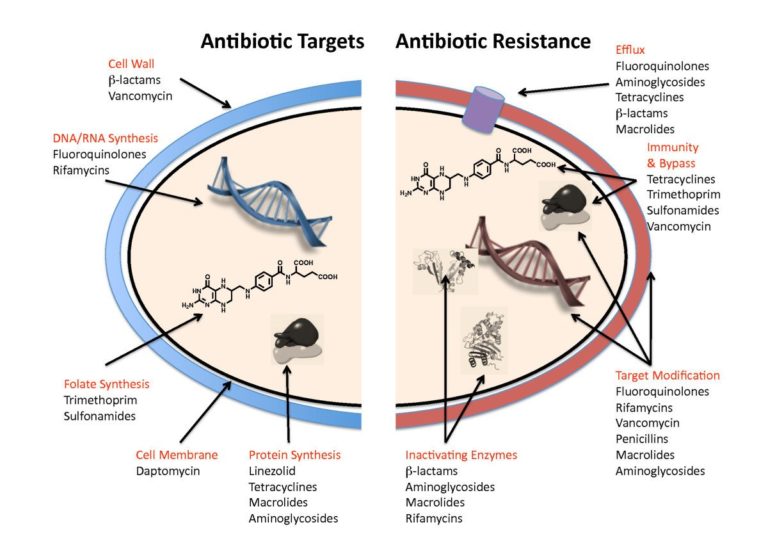
Wright, D.S. (n.d.). Figure 1: Diagram to summarise the main targets of antibiotics in bacterial cells, and the main mechanism of antibiotic resistance. https://www.futurelearn.com/info/courses/introduction-to-microbiology/0/steps/51440
Databases
-
World Book Encyclopedia This link opens in a new window
 Online version of the complete reference work along with dictionary, atlas, links, magazines, historical documents, audio, video, images, and 3D photograph
Online version of the complete reference work along with dictionary, atlas, links, magazines, historical documents, audio, video, images, and 3D photograph
-
Britannica Schools This link opens in a new window
 Britannica School covers the core subject areas of English, Maths, Science and History. Interactive lessons, activities, games, stories, worksheets, manipulatives, study guides and research tools.
Britannica School covers the core subject areas of English, Maths, Science and History. Interactive lessons, activities, games, stories, worksheets, manipulatives, study guides and research tools.
How do antibiotics work?
Twig. (n.d.). Antibiotics. https://www-twig-world-com.db.scotch.wa.edu.au/film/glossary/antibiotic-241/
Drugs used to treat bacterial infections by killing or inhibiting the growth of bacteria.They do not work against viruses or fungi, and so cannot treat many other infections. Source: Twig Database
Do I need antibiotics for a virus infection or bacterial infection?
-
Differences between bacterial and viral infections. (2016, May). Retrieved March 1st, 2018, from Health Direct.: https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/bacterial-vs-viral-infection
 Website gives a simple answer in point form.
Website gives a simple answer in point form. -
Do I need an antibiotic? (2017, Feb 1at). Retrieved March 1st, 2018, from Healthy Me PA: https://www.healthymepa.com/2017/02/21/do-you-need-antibiotics/
 Simple explanation using good visual aids. Recent information. Easy to understand.
Simple explanation using good visual aids. Recent information. Easy to understand. -
Infections - bacterial and viral. (2014, March). Retrieved March 1st, 2018, from Better Health Channel: https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/infections-bacterial-and-viral
 Detailed outline of bacterial and viral infections. Need to read the whole article carefully to find the answer to the question.
Detailed outline of bacterial and viral infections. Need to read the whole article carefully to find the answer to the question.
What is the best way to take antibiotics?
-
Using medication: using antibiotics correctly and avoiding resistance. (2017). Retrieved March 1st, 2018, from Pub Med Health: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0087079/
 Though most of the article is about resistance, at the bottom of the page is some clear guidance in relation to taking antibiotics.
Though most of the article is about resistance, at the bottom of the page is some clear guidance in relation to taking antibiotics. -
When and how to take antibiotics. (2014). Retrieved March 1st, 2018, from Alliance of Prudent Use of Antibiotics: http://emerald.tufts.edu/med/apua/about_issue/when_how.shtml
 Well organized outline of the topic. Uses clear language. Short article only however.
Well organized outline of the topic. Uses clear language. Short article only however.
Antibiotic Resistance
Twig. (n.d.). Antibiotic resistance. https://www-twig-world-com.db.scotch.wa.edu.au/film/glossary/antibiotic-resistance-242/
Video on the ability of bacteria to survive exposure to an antibiotic, often by producing a protein that disables or prevents transport of the antibiotic into the cell. Source: Twig Database.

